Data Model¶
In Elgg, everything runs on a unified data model, based on atomic units of data called entities.
Plugins are strongly discouraged from dealing with database issues themselves, which makes for a more stable system that also has visible benefits for the end user. Content created by different plugins can be mixed together in consistent ways, which are programmed using generic principles - in other words, plugins are faster to develop, and are at the same time much more powerful.
Every entity in the system inherits the ElggEntity class. This class controls access permissions, ownership and so on. see ElggUser
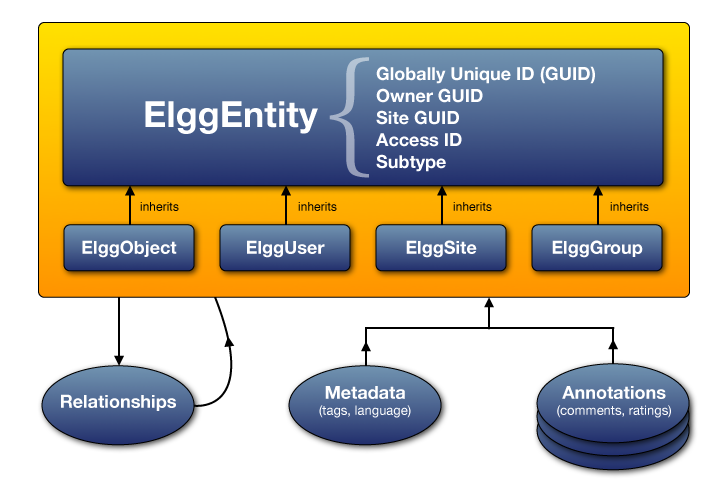
Entities¶
ElggEntity has four main specializations, which provide extra properties and methods to more easily handle different kinds of data. Render an entity with View an entity
ElggObject¶
Usually content like blog posts, uploaded files and bookmarks
ElggUser¶
each user in the system
ElggSite¶
each site within an Elgg install
ElggGroup¶
multi-user collaborative systems, which were called Communities in prior versions of Elgg
Relationships¶
The ElggRelationship class allows you to quickly establish connections between entities. A user can “friend” another user. A user can join a group. A photo can be tagged to indicate a user is in that photo. All of this and more can be done with the ElggRelationship class.
Annotations and metadata¶
You can extend entities with extra information in two ways:
- Metadata This is information you can add to an object to describe it further. For example, tags, an ISBN number, a file location or language information would fall under metadata.
- Annotations Information generally added by third parties which adds to the information provided by the entity. For example, comments and ratings are both annotations.